Batch Job IoT Device: Making Sense Of Group Operations
Running a system with many connected things, often called IoT devices, can sometimes feel like trying to manage a very large, busy family. Each device has its own job, but sometimes you need them all to do something at once, or at least in groups. This is where the idea of a batch job IoT device comes into play, offering a smart way to handle tasks for many devices together. It's about getting things done efficiently, especially when you have a whole fleet of gadgets out there working for you.
Think about it: sending individual commands to hundreds, or even thousands, of tiny sensors or smart gadgets can be a real headache. It takes time, uses up network space, and can be pretty unreliable if one device isn't ready. A batch job, in this setting, is essentially a plan to perform a set of operations on a collection of devices, or process a collection of data from them, all in one go, or in carefully managed chunks. It helps keep things tidy and running smoothly, you know?
This approach isn't just for big companies with lots of equipment; even smaller setups can benefit from understanding how to group tasks for their connected items. It helps save power, reduces the amount of network chatter, and generally makes managing your IoT world a bit easier to handle. We're going to look closer at how this works and why it's a very good thing for anyone working with IoT today, and apparently, it's something many people wonder about.
Table of Contents
- What Are Batch Jobs in IoT?
- Why Batch Processing Matters for IoT Devices
- Real-World Scenarios and Benefits
- How Batch Jobs Work with IoT Devices
- Tips for Effective Batch Job Implementation
- Frequently Asked Questions About Batch Job IoT Devices
- Moving Forward with Batch Jobs in IoT
What Are Batch Jobs in IoT?
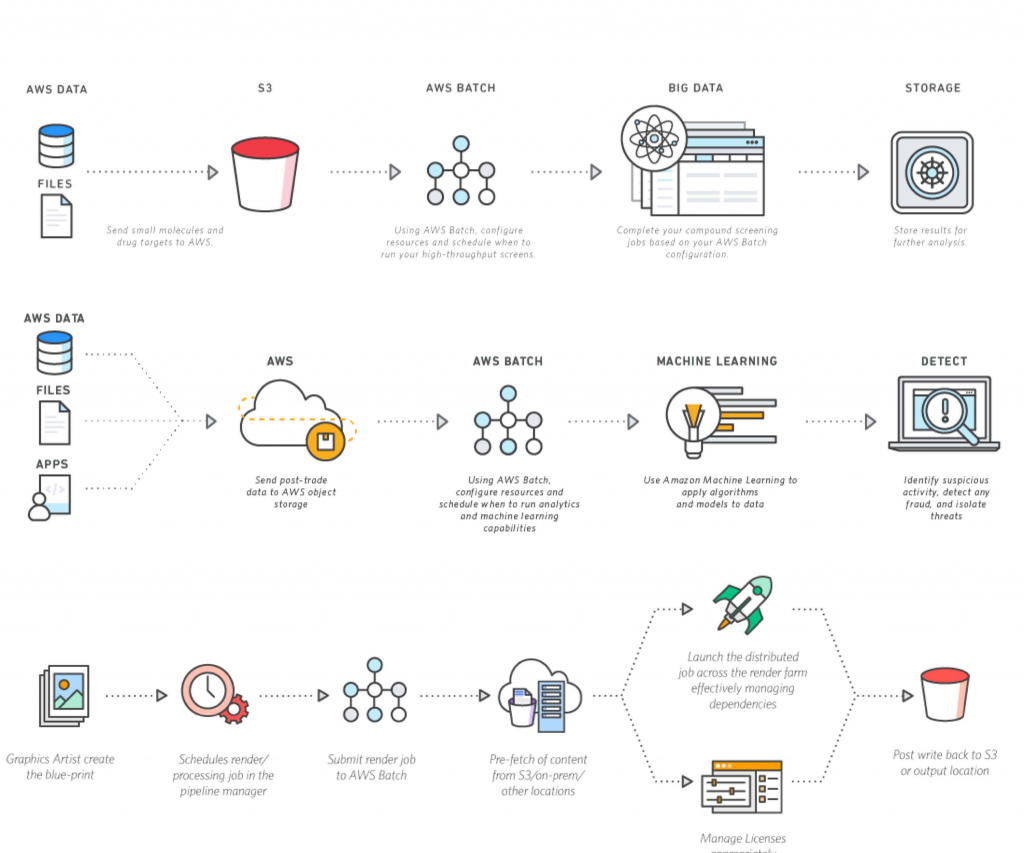
A batch job, when we talk about IoT devices, is a scheduled operation that applies a particular action or series of actions to a group of devices, rather than one at a time. It’s like sending out a single instruction that many devices will pick up and act upon when they are ready. This could involve updating software, changing settings, collecting specific data, or even telling devices to turn on or off at a certain moment. It’s a very practical way to manage a large number of connected items.
Imagine you have a hundred smart light bulbs spread across a building. If you needed to change their brightness setting, doing it one by one would be pretty tedious. A batch job lets you send that brightness command to all hundred bulbs at once. They might not all respond at the exact same millisecond, but the system handles the distribution and tracking for you. This kind of grouped activity is, so, a core part of efficient IoT management.
The core idea here is to process things in chunks. Just like some older computer systems would process a "list" of commands, as mentioned in "My text" with "For %%a in (list) do command parameters," an IoT batch job processes a list of devices or a list of tasks. This list can be quite varied, containing different elements that need the same action. It really helps organize what can otherwise be a very chaotic situation.
- Breckie Hill Leaked Only Fans
- Jackerman Mothers Warmth 3 Release Date
- Deephotlink
- Jon Skoog Net Worth
- Hanalei Swan The 30m Shark Tank Deal She Turned Down Ndash What Happened
This method helps manage resources more effectively. Instead of constant, small trickles of information, you get larger, more controlled bursts. This can be better for network traffic and for the devices themselves, especially those with limited battery life or processing power. It’s about being smart with how and when you ask your devices to do things, which is a bit of a strategic move.
Why Batch Processing Matters for IoT Devices
Batch processing for IoT devices is important for several good reasons, primarily around efficiency, reliability, and cost control. When you have many devices, the traditional way of talking to each one individually can become quite difficult to maintain. It's like trying to have a separate conversation with everyone at a large party all at once; it just doesn't work out very well.
One big reason is network traffic. Sending small, individual messages constantly can clog up your network, especially if devices are using cellular data or limited Wi-Fi. Batching these tasks means fewer, larger data transfers, which can be much more efficient. It’s a bit like sending one big package instead of many tiny envelopes, which can save a lot on postage, you know?
Another point is power use. Many IoT devices run on batteries and need to save every bit of energy they can. Waking up frequently to check for individual commands or send small bits of data uses a lot of power. With batch jobs, devices can wake up less often, receive a whole set of instructions or send a chunk of data, and then go back to sleep. This significantly extends battery life, which is a very big deal for remote sensors or devices in hard-to-reach places.
Reliability is also a key factor. When you send commands in a batch, the system can often confirm that all devices in the group have received and acted upon the instruction. If a device misses an update, the system knows and can try again later, perhaps as part of the next batch. This contrasts with a simple "fire and forget" approach, which might leave some devices out of sync. This helps make sure everything is more or less working as it should.
Finally, there's the cost aspect. Less network usage often means lower data bills. Longer battery life means fewer trips to replace batteries, saving on labor and parts. And a more reliable system means less troubleshooting and fewer headaches for the people managing it. So, it's pretty clear that batch processing offers a lot of practical advantages for IoT deployments today.
Real-World Scenarios and Benefits
Thinking about how batch jobs actually play out in the real world helps show just how useful they are for IoT devices. There are many situations where grouping tasks together just makes a lot of sense, helping businesses and organizations run more smoothly. It’s not just about theoretical gains; these are very real improvements.
Software Updates for a Fleet of Devices
Imagine a company that has thousands of smart meters installed in homes across a city. From time to time, these meters need software updates to fix issues or add new features. Sending updates one by one would be a truly massive undertaking. With a batch job, the update package can be sent to all meters in a specific area, or all meters of a certain model, at once. The meters download and install the update when they are able, perhaps during off-peak hours to avoid network congestion. This ensures that all devices eventually get the needed improvements without overwhelming the system. It's a much more manageable way to handle things, actually.
Collecting Data from Remote Sensors
Consider a network of environmental sensors in a vast agricultural field, monitoring soil moisture and temperature. These sensors might only need to report data a few times a day to conserve power. Instead of each sensor sending tiny bits of data whenever it feels like it, a batch job can instruct them to collect data for a set period and then send all of it together at a specific time. This consolidates data transmission, making it more efficient and reliable. It’s a bit like gathering all your mail and sending it in one trip to the post office, rather than many small trips, you know?
Changing Device Configurations
A smart building might have hundreds of smart thermostats, light switches, and security cameras. If the building manager needs to adjust the heating schedule for all thermostats on a particular floor, or change the recording settings for all cameras in a certain wing, a batch job is the answer. A single command set can be pushed to all relevant devices, ensuring consistency and saving a lot of manual effort. This helps maintain order and consistency across the whole setup, which is something very important.
Benefits You Can Feel
- Reduced Network Load: Fewer, larger data transfers mean less strain on your network infrastructure.
- Improved Battery Life: Devices spend less time actively transmitting or receiving, stretching out their operational time.
- Higher Reliability: Systems can better track success and failure rates for grouped operations, allowing for retries and better overall management.
- Operational Efficiency: Less manual intervention is needed, freeing up staff for other important tasks.
- Cost Savings: Lower data usage and less maintenance work can lead to significant financial benefits.
How Batch Jobs Work with IoT Devices
The way batch jobs work with IoT devices involves a few key steps, usually orchestrated by a central management platform. It's not just about sending out a command; there's a bit more to it, making sure everything goes as planned. This process tries to make sure things "block safely," as "My text" hints at, so parts of the operation don't interfere with each other unexpectedly.
Setting Up the Batch
First, you define the "batch." This involves picking which devices will be part of the group and what action they need to take. It could be "all temperature sensors in Warehouse A" or "all smart locks that need a firmware update." The system creates a list of these devices, much like the "list of any elements" mentioned in "My text" for batch files. You also specify the command or data to be sent, such as a new software version or a configuration file.
Distribution and Execution
Once the batch is defined, the management platform begins to distribute the job. This might happen immediately, or it could be scheduled for a specific time, like overnight when network traffic is low. Devices receive the command or data package. They then process it. This processing can involve downloading a file, applying settings, or running a small script. The system tries to send the command to as many devices as possible, considering things like device memory, because "the batch size should pretty much be as large as possible without exceeding memory," as "My text" points out. This helps avoid issues where devices might struggle to handle too much at once.
Handling Responses and Errors
After a device processes its part of the batch job, it usually sends back a status report. This report tells the management platform whether the job was successful, if there were any errors, or if the device is still working on it. This feedback is very important. If something "was unexpected at this time," as "My text" mentions in a different context, the system can log that and potentially try again later. It’s about making sure the system can track progress and deal with problems. You might also need to think about how to implement conditional checks, a bit like using logical operators for "neq, lss, gtr" that are talked about in "My text," to make sure certain steps only happen if previous ones succeed.
Monitoring and Completion
The central platform continuously monitors the progress of the batch job. It tracks which devices have completed the task, which are still pending, and which have reported errors. This allows administrators to see the overall health of the operation and intervene if necessary. Once all devices have reported in, or a set time limit is reached, the batch job is marked as complete. This structured way of working is much better than systems that have "no concept of sections to control flow," which can lead to messy outcomes.
In a way, it’s similar to how large data processing systems handle "Epoch, Batch Size, and Iteration," as noted in "My text." You process a chunk of work (a batch) over a certain period or multiple attempts (iterations) to get to a desired outcome. This layered approach helps manage the large scale of IoT effectively, and you know, it just makes things a lot simpler.
Tips for Effective Batch Job Implementation
Getting batch jobs right for your IoT devices can save you a lot of trouble, but it does take some careful thought. It's not just about sending out a command and hoping for the best. Here are some pointers to help you make your batch operations work well, which is a very good thing to consider.
Start Small and Test Thoroughly
Before you push a batch job to thousands of devices, it's a very good idea to test it on a small group first. Pick a few devices that represent your different types or setups. This helps you catch any unexpected issues or errors in a controlled environment. Think of it like a pilot program; you learn what works and what doesn't before rolling it out widely. This helps avoid problems that might be "unexpected at this time" on a larger scale.
Consider Device Capabilities and Network Conditions
Not all IoT devices are created equal. Some have very limited memory, processing power, or network bandwidth. When planning a batch job, especially for updates or large data transfers, make sure the "batch size should pretty much be as large as possible without exceeding memory" on the devices. Also, think about the network where your devices operate. Are they on a stable Wi-Fi connection, or are they using cellular data in a remote area? Schedule large transfers during off-peak hours if possible. This helps ensure your operations go smoothly.
Implement Robust Error Handling and Retries
Things can and do go wrong. A device might be offline, lose power, or encounter a software glitch. Your batch job system should be set up to handle these situations gracefully. This means logging errors, attempting retries for failed devices, and providing clear status reports. A good system will let you know which devices didn't complete the task so you can address them specifically. It's about building in resilience, so things don't completely fall apart if one part fails.
Plan for Rollbacks
Sometimes, an update or configuration change might cause unintended problems. It's wise to have a plan for rolling back changes if something goes wrong. This could mean having a previous software version readily available to push out as another batch job, or a way to revert settings. This safety net can save a lot of headaches and downtime, you know?
Monitor and Analyze Performance
Once your batch jobs are running, keep an eye on them. Are they completing on time? Are there many errors? Is network usage spiking unexpectedly? Monitoring helps you understand the impact of your batch operations and lets you fine-tune them for better performance. Regularly reviewing these metrics can help you improve your strategy over time, and it’s a really important step.
Secure Your Batch Operations
Because batch jobs can affect many devices at once, securing them is very important. Make sure only authorized personnel can initiate or modify batch jobs. Use strong encryption for data transferred during batch operations and ensure devices authenticate properly before accepting commands. This helps prevent malicious actors from gaining control over your devices. For more information on securing your IoT environment, Learn more about IoT security on our site, which is something we talk about a lot.
Frequently Asked Questions About Batch Job IoT Devices
People often have questions when they first start thinking about batch jobs for their IoT setups. Here are some common ones that come up, which is very natural.
What is a batch job in IoT?
A batch job in IoT is a planned operation where a single set of commands or data is sent to a group of connected devices at once, or in managed chunks, rather than individually. It helps with things like updating software, changing settings, or gathering data from many devices efficiently. It’s about grouping tasks for better management, so it’s a pretty smart way to do things.
Why use batch processing for IoT devices?
Using batch processing for IoT devices helps save network bandwidth, extend device battery life, improve the reliability of operations, and generally make managing a large number of devices much easier and more cost-effective. It reduces the need for constant, small communications, making the whole system more stable and efficient. It’s a very practical choice for many setups.
How do you implement batch updates for IoT devices?
Implementing batch updates for IoT devices usually involves using an IoT management platform. You select the devices that need updating, upload the new software or configuration, and then schedule the batch job. The platform handles sending the update to the chosen devices, tracking their progress, and reporting any issues. Devices download and install the update when they are able, often reporting back their success or failure. It's a structured way to push changes to many devices at once, and you know, it just works better.
Moving Forward with Batch Jobs in IoT
As the number of connected devices continues to grow, the need for smart, efficient ways to manage them becomes more and more clear. Batch jobs offer a very powerful solution for handling large-scale operations, from keeping software up-to-date to collecting important data. They help businesses and organizations keep their IoT deployments running smoothly, saving time, money, and effort. It's about working smarter, not harder, with your devices, and that's a pretty good goal.
Understanding the basics of how these jobs work, why they are beneficial, and how to put them into practice can really make a difference in how you approach your IoT projects. It’s a very practical skill to have as more and more things get connected. You can find more details about various IoT management strategies and tools on this page on our site, which might be helpful.
As of today, , the focus on efficient and scalable IoT management is stronger than ever. Batch jobs are not just a nice-to-have; they are becoming a very essential part of keeping large IoT systems healthy and performing well. It's about making sure your connected devices are always ready for what's next, and that's a truly valuable thing.
- Jasmine Crockett Husband And Children
- Link Somali Telegram 2025
- Jameliz Benitez Only Fans
- Lia Engel Onlyfans Leaks
Unlock Insights: Remote IoT Batch Jobs Explained

Remote IoT Batch Job Example: Revolutionizing Automation With AWS

Boost IoT With Batch Jobs: Execution Guide & Best Practices